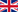
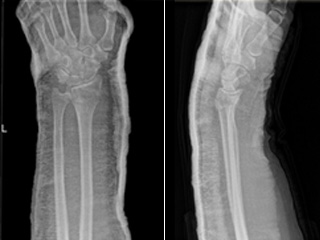
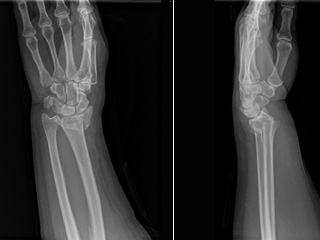
The fracture of the distal radius is the most frequent bone lesions treated by the orthopedic surgeon.
The most frequent mechanism is the fall of their own height in elderly patients or traffic accidents in the case of younger patients.
Most fractures are treated conservatively by reduction under local anesthesia by the traumatologist and splinting for at least 6 weeks or in small percentages by surgical treatment with kishner needles, plate and screws or external fixators according to the type and location of the fracture.
Clinically the patient goes to hospital with severe pain with deformity and functional impotence of the wrist and after being evaluated by the medical team, the image study is completed by anteroposterior and lateral radiographs that will be evaluated by the orthopedic surgeon who will take the treatment decision definitive according to the type of injury.
After orthopedic or surgical treatment, the patient usually needs rehabilitation treatment that can be done on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a physiotherapist and in many cases a bone quality study should be done since older patients have a high risk that in the future they will have other osteoporotic fractures in which case it is necessary to start antiresorbtivo treatment and osteoformador.